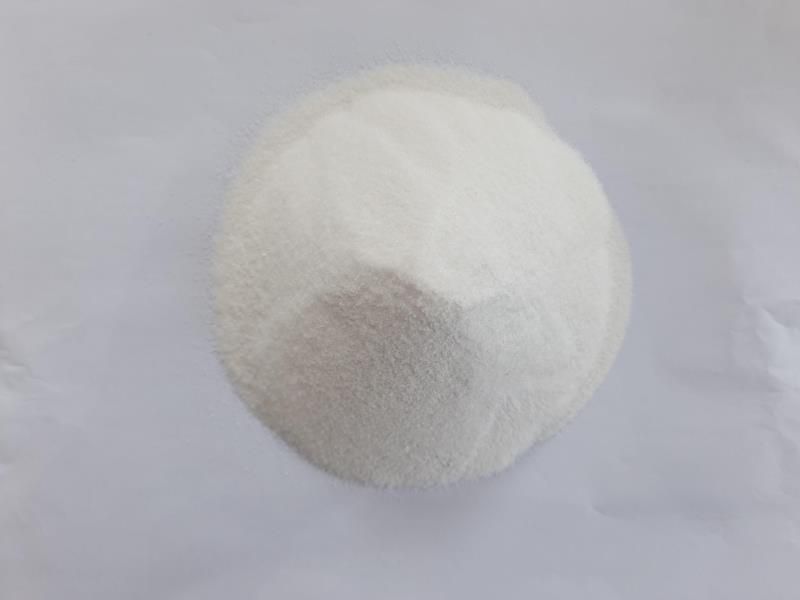
Using cryolite as solvent, alumina is dissolved and then electrolyzed. Cryolite plays a key role here. It solves the difficulties of alumina with high melting point (up to 2050 ℃), non-conductive and unable to be electrolyzed alone. After alumina is dissolved in cryolite, it can be electrolyzed at a temperature of (940 ℃ ~ 980 ℃). Cryolite has other wonderful functions. It is lighter than aluminum in the molten state. The aluminum obtained by electrolysis sinks at the bottom of the tank and cryolite floats on it, which plays a role in preventing aluminum from being oxidized by air.